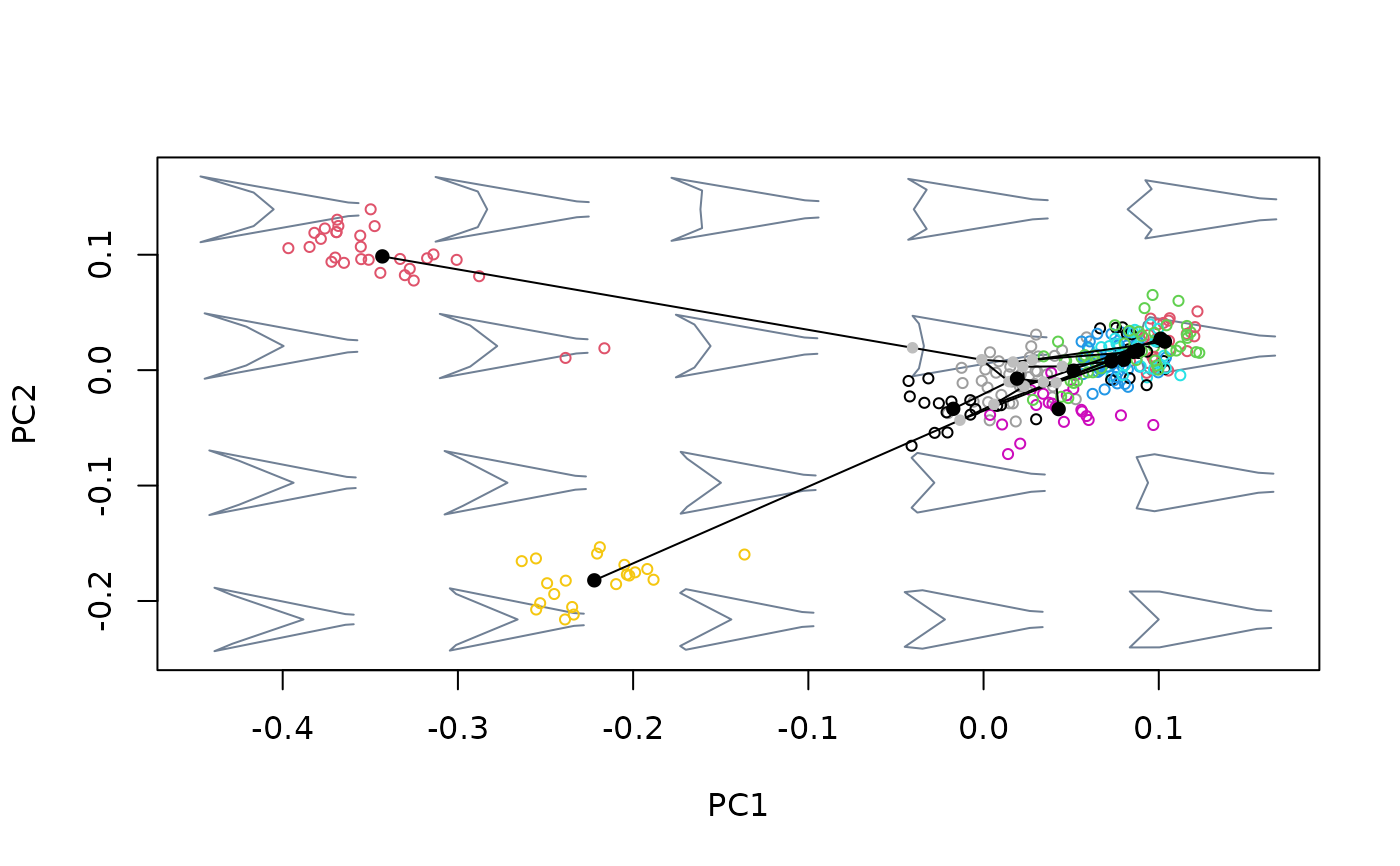
Project phylogenetic relationships among a set of shapes (representing the tips of a phylogenetic tree) into an existing bivariate morphospace.
proj_phylogeny(
mspace,
shapes = NULL,
tree,
pipe = TRUE,
pch.nodes = 16,
col.nodes = "gray",
bg.nodes = 1,
cex.nodes = 0.8,
pch.tips = 16,
bg.tips = 1,
col.tips = 1,
cex.tips = 1,
...
)Arguments
- mspace
An
"mspace"object.- shapes
Shape data, with 3rd margin names matching tip labels from
tree.- tree
A
"phylo"object containing a phylogenetic tree.- pipe
Logical; is the function being included in a pipe?
- pch.nodes
Symbol of the scatter points corresponding to the nodes of the phylogeny.
- col.nodes
Color of the hulls/ellipses and/or scatter points corresponding to the nodes of the phylogeny.
- bg.nodes
Background color of the scatter points corresponding to the nodes of the phylogeny.
- cex.nodes
Numeric; size of the scatter points corresponding to the nodes of the phylogeny.
- pch.tips
Symbol of the scatter points corresponding to the tips of the phylogeny.
- bg.tips
Background color of the scatter points corresponding to the tips of the phylogeny.
- col.tips
Color of the hulls/ellipses and/or scatter points corresponding to the tips of the phylogeny.
- cex.tips
Numeric; size of the scatter points corresponding to the tips of the phylogeny.
- ...
Further arguments passed to
graphics::lines()(commonly,pch,col/bgandcex.
Value
If a plot device with a morphospace is open, shapes representing the
tips and nodes of the phylogenetic tree, as well as the lines connecting
them, are projected into morphospace. If pipe = FALSE scores for
nodes and tips of the phylogeny are returned invisibly.
If pipe = TRUE the supplied "mspace" object will be modified
by appending a $phylo_Scores and a $phylo slots to
$projected, as well as by adding some graphical parameters (stored
into the $plotinfo slot), and returned invisibly.
Details
The purpose of this function is twofold. First, it is meant to
transform a morphospace into a phylomorphospace by projecting node shapes
and phylogenetic relationships. To this end, a set of named shapes must be
provided; dim(shapes)[3] must match tree$tip.labels. Second,
this function can be used to retrieve the scores corresponding to nodes of
the phylogenetic tree ($projected$phylo_scores, which can then be
used to compute the node shapes using extract_shapes. The
position of these shapes in morphospace is estimated using the
squared-changes parsimony algorithm as performed by phytools::fastAnc().
Examples
#load and extract relevant data, packages and information
library(magrittr)
data("tails")
shapes <- tails$shapes
species <- tails$data$species
sp_shapes <- expected_shapes(shapes, species)
tree <- tails$tree
links <- tails$links
#generate basic morphospace, add sampled shapes, species mean shapes, and
#phylogenetic structure
mspace(shapes, links = links, mag = 0.7, axes = c(1,2), cex.ldm = 0) %>%
proj_shapes(shapes = shapes, col = c(1:13)[species], pch = 1,
cex = 0.7) %>%
proj_phylogeny(shapes = sp_shapes, tree = tree)